Attention Is All You Need
URL: http://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762
Zotero Link: arXiv Fulltext PDF
Topics: NLP, Transformers, LLM, Attention
Formatted Bibliography
Vaswani, Ashish, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N. Gomez, Lukasz Kaiser, and Illia Polosukhin. “Attention Is All You Need.” arXiv, December 5, 2017. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1706.03762.
Abstract
The dominant sequence transduction models are based on complex recurrent or convolutional neural networks in an encoder-decoder configuration. The best performing models also connect the encoder and decoder through an attention mechanism. We propose a new simple network architecture, the Transformer, based solely on attention mechanisms, dispensing with recurrence and convolutions entirely. Experiments on two machine translation tasks show these models to be superior in quality while being more parallelizable and requiring significantly less time to train. Our model achieves 28.4 BLEU on the WMT 2014 English-to-German translation task, improving over the existing best results, including ensembles by over 2 BLEU. On the WMT 2014 English-to-French translation task, our model establishes a new single-model state-of-the-art BLEU score of 41.8 after training for 3.5 days on eight GPUs, a small fraction of the training costs of the best models from the literature. We show that the Transformer generalizes well to other tasks by applying it successfully to English constituency parsing both with large and limited training data.
Notes
Pass 1 略读
Q1 简单总结论文想要干嘛?
提出Transformer结构,全部基于Attention,不需要RNN和CNN
Q2 这是否是新领域?如何归类?之前的研究有什么不足?
不是新领域,之前有过相关工作。但是RNN无法高效并行,处理长句子尤其明显。之前的Attention也不能脱离RNN单独工作。
Pass 2 全面了解
Q3 论文提出的解决方案的关键点都是?
- Encoder-Decoder结构
- Attention Block
- Self-Attention
- Multihead Attention
- Position Encoding
Q4 论文想要验证的假设是?
只使用Attention的Transformer结构可以更好地并行训练以及在NLP的任务(e.g. 机器翻译)中取得更好的效果
Q5 论文的实验和结果有没有很好地支持要验证的假设?
有,并行和效果都有提高。
Pass 3 精读
Q6 论文的方案具体是怎么做的?能否用一个例子过一遍整个pipeline?
Q7 论文的实验是如何设计的?
- 通过比较在机器翻译的数据集上的表现,和之前的SOTA模型比较BLEU Score和Training Cost(FLOPs)
- 也测试了不同hyperparameters的表现,比较了PPL和BLEU Score
- 同时测试了在English Constituency Parsing的表现来证明可以适用于其他NLP任务
Q8 论文的核心贡献到底是什么?
- 全新的Transformer结构,可以用于各种NLP任务,并行度高,效果好
- 全部基于Attention,不再需要CNN和RNN
(Optional) 研究领域相关工作调研
Q9 下一步能做什么?
将Transformer结构用于各种任务、预训练语言模型
Q10 有哪些相关的研究需要关注?
本文提出Transformer是后续著名LLM例如BERT、GPT等的鼻祖。
Q11 使用了什么数据集/工具/评估方法?代码是否开源可复现?
使用了一些机器翻译的数据集进行测试,代码开源,目前热门的实现是HuggingFace Transformers
其他评价
NLP大模型时代的奠基作,必读。
Highlights
The dominant sequence transduction models are based on complex recurrent or convolutional neural networks that include an encoder and a decoder. The best performing models also connect the encoder and decoder through an attention mechanism. (Page 1)
总结之前处理序列的主流工作: CNN或RNN+encoder-decoder结构,最新的工作还加上了Attention的机理
We propose a new simple network architecture, the Transformer, based solely on attention mechanisms, dispensing with recurrence and convolutions entirely. (Page 1)
本文的工作: 提出了Transformer结构,全部依靠Attention,不需要CNN和RNN
Experiments on two machine translation tasks show these models to be superior in quality while being more parallelizable and requiring significantly less time to train. (Page 1)
实验结构表明,效果好且好训练
We show that the Transformer generalizes well to other tasks by applying it successfully to English constituency parsing both with large and limited training data. (Page 1)
也可以应用到其他相关任务
This inherently sequential nature precludes parallelization within training examples, which becomes critical at longer sequence lengths, as memory constraints limit batching across examples. (Page 2)
RNN的缺陷,无法并行处理训练数据,在处理长句子时尤其明显
In all but a few cases [27], however, such attention mechanisms are used in conjunction with a recurrent network. (Page 2)
之前的工作里Attention都和RNN一起
The goal of reducing sequential computation (Page 2)
all of which use convolutional neural networks as basic building block, computing hidden representations in parallel for all input and output positions. (Page 2)
In these models, the number of operations required to relate signals from two arbitrary input or output positions grows in the distance between positions, linearly for ConvS2S and logarithmically for ByteNet. This makes it more difficult to learn dependencies between distant positions [12]. (Page 2)
前作尝试并行处理hidden representation计算,但是计算距离远的两个位置需要更多训练资源。Transformer通过多头注意力来解决这个问题
an encoder-decoder structure [5, 2, 35]. Here, the encoder maps an input sequence of symbol representations (x1, ..., xn) to a sequence of continuous representations z = (z1, ..., zn). Given z, the decoder then generates an output sequence (y1, ..., ym) of symbols one element at a time. At each step the model is auto-regressive [10], consuming the previously generated symbols as additional input when generating the next. (Page 2)
介绍encoder-decoder结构
using stacked self-attention and point-wise, fully connected layers for both the encoder and decoder, (Page 2)
简单来说Transformer就是self-attention+全连接
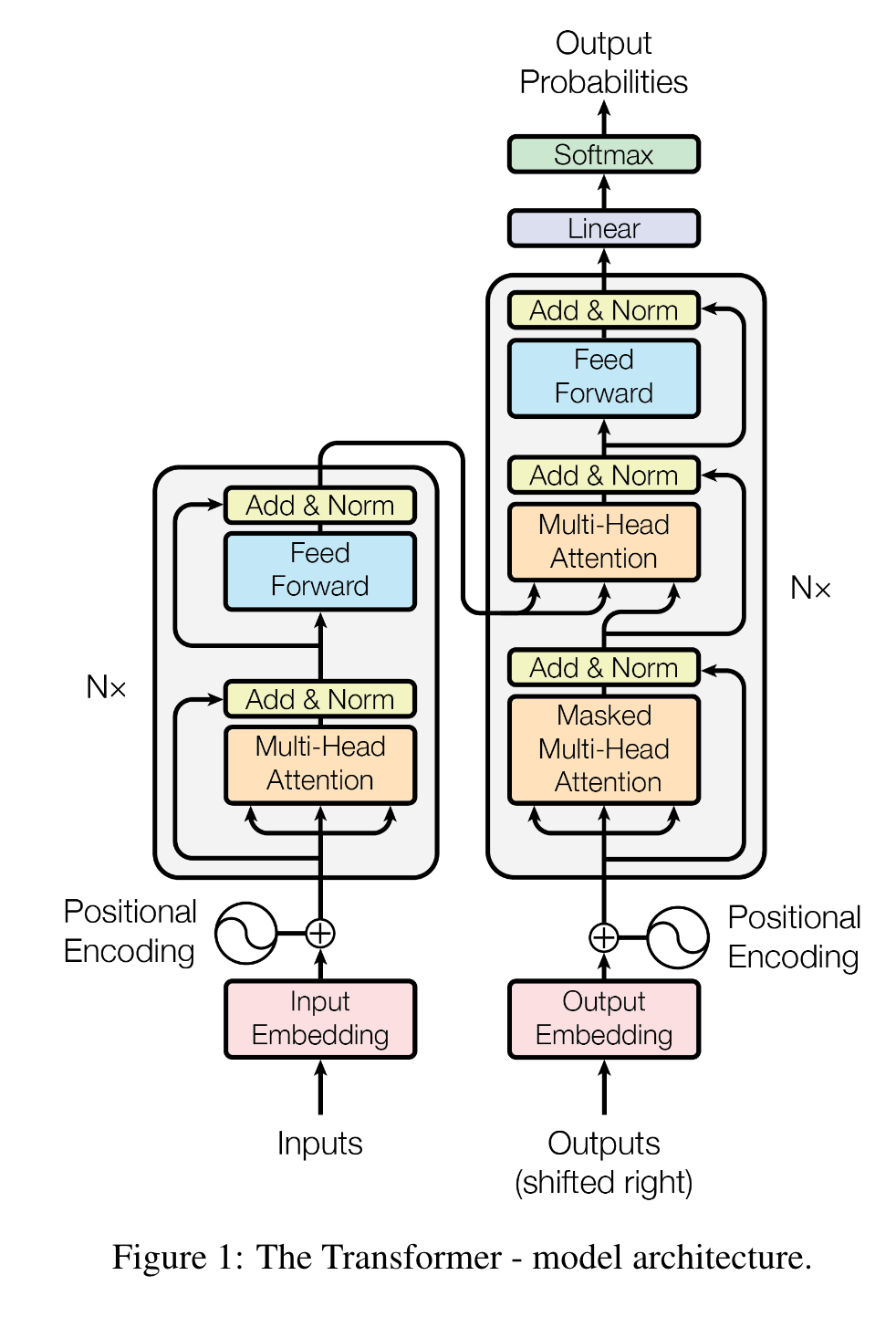 Transformer经典结构图
Transformer经典结构图
The first is a multi-head self-attention mechanism, and the second is a simple, positionwise fully connected feed-forward network. We employ a residual connection [11] around each of the two sub-layers, followed by layer normalization [1]. (Page 3)
encoder有6个block,每个block有两层,第一层是多头自注意力,第二层是全连接feed-forward(MLP),每层都用残差连接一个layer norm
That is, the output of each sub-layer is LayerNorm(x + Sublayer(x)), where Sublayer(x) is the function implemented by the sub-layer itself. (Page 3)
produce outputs of dimension dmodel = 512. (Page 3)
In addition to the two sub-layers in each encoder layer, the decoder inserts a third sub-layer, which performs multi-head attention over the output of the encoder stack. (Page 3)
decoder也是6个block,每个block在encoder的基础上多加了一个多头注意力来结合encoder传来的输入和output已经产生的输出作为新的输入。同时对output部分的attention加了mask处理
We also modify the self-attention sub-layer in the decoder stack to prevent positions from attending to subsequent positions. This masking, combined with fact that the output embeddings are offset by one position, ensures that the predictions for position i can depend only on the known outputs at positions less than i. (Page 3)
i位置只能attendi之前的位置
An attention function can be described as mapping a query and a set of key-value pairs to an output, where the query, keys, values, and output are all vectors. The output is computed as a weighted sum of the values, where the weight assigned to each value is computed by a compatibility function of the query with the corresponding key. (Page 3)
Attention是将q、k、v输入得到一个加权和作为输出。权重从q和k计算得到。
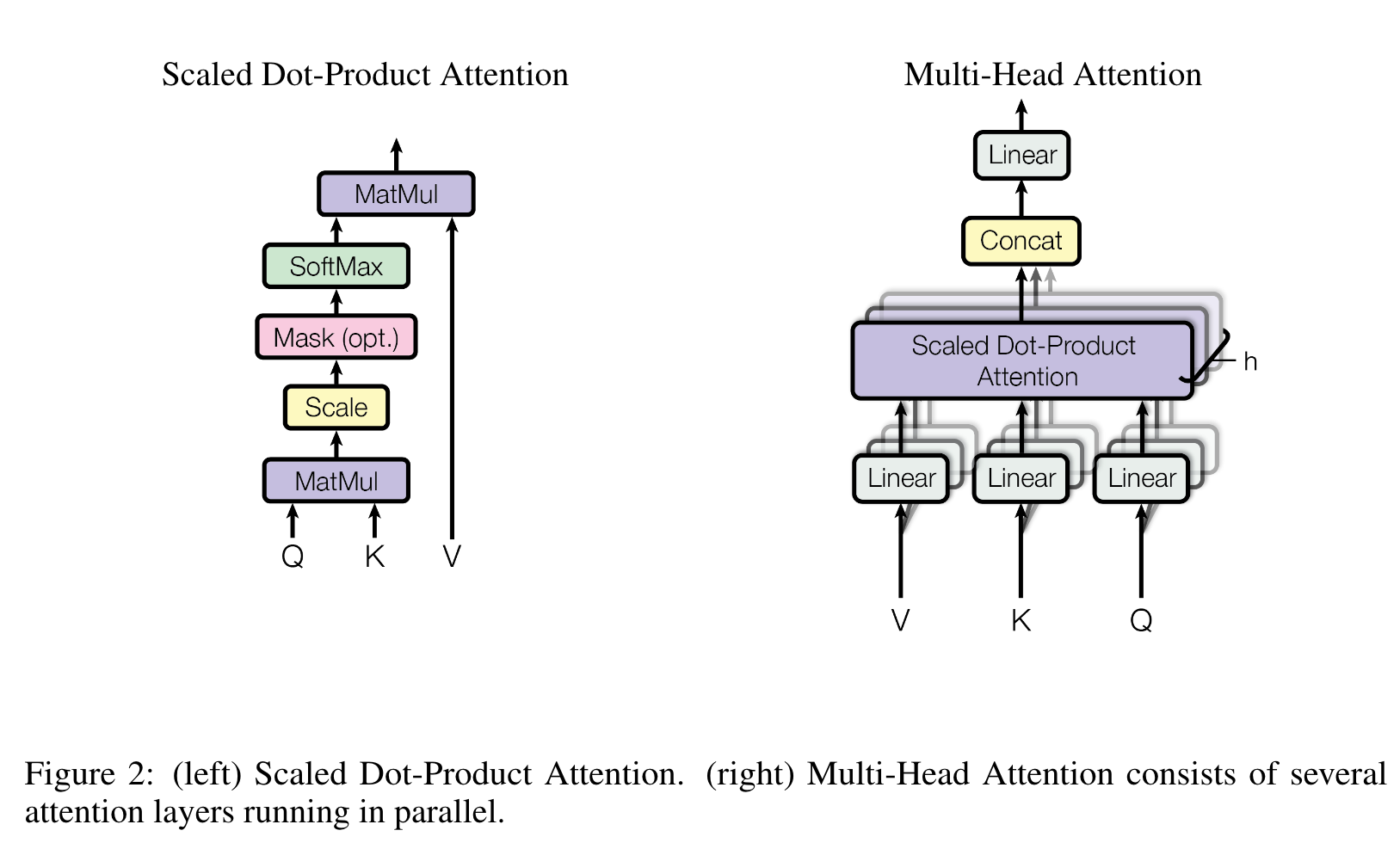
The input consists of queries and keys of dimension dk, and values of dimension dv. We compute the dot products of the query with all keys, divide each by √dk (Page 4)
scale by sqrt(dk)
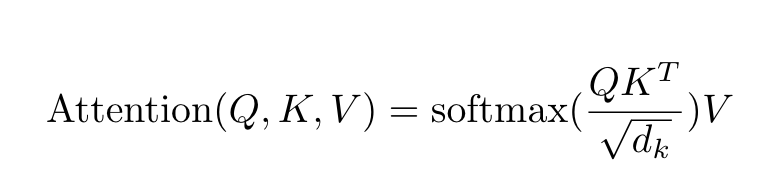
dot-product attention is much faster and more space-efficient in practice, since it can be implemented using highly optimized matrix multiplication code. (Page 4)
we found it beneficial to linearly project the queries, keys and values h times with different, learned linear projections to dk, dk and dv dimensions, respectively. (Page 4)
每个qkv都投影出dimension个qkv,然后并行进行多头attention,把输出再拼起来得到dv维的向量的输出
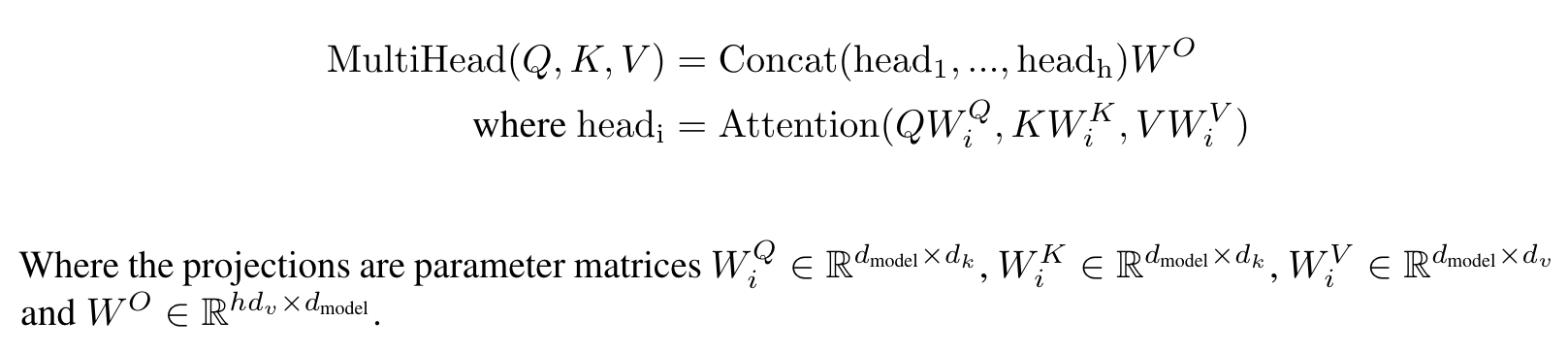
In this work we employ h = 8 parallel attention layers, or heads. For each of these we use dk = dv = dmodel/h = 64. (Page 5)
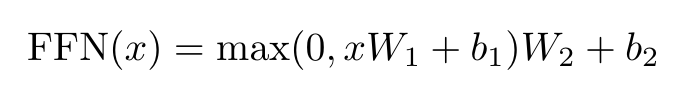
The dimensionality of input and output is dmodel = 512, and the inner-layer has dimensionality dff = 2048. (Page 5)
we use learned embeddings to convert the input tokens and output tokens to vectors of dimension dmodel. We also use the usual learned linear transformation and softmax function to convert the decoder output to predicted next-token probabilities (Page 5)
The positional encodings have the same dimension dmodel as the embeddings, so that the two can be summed. There are many choices of positional encodings, learned and fixed (Page 6)
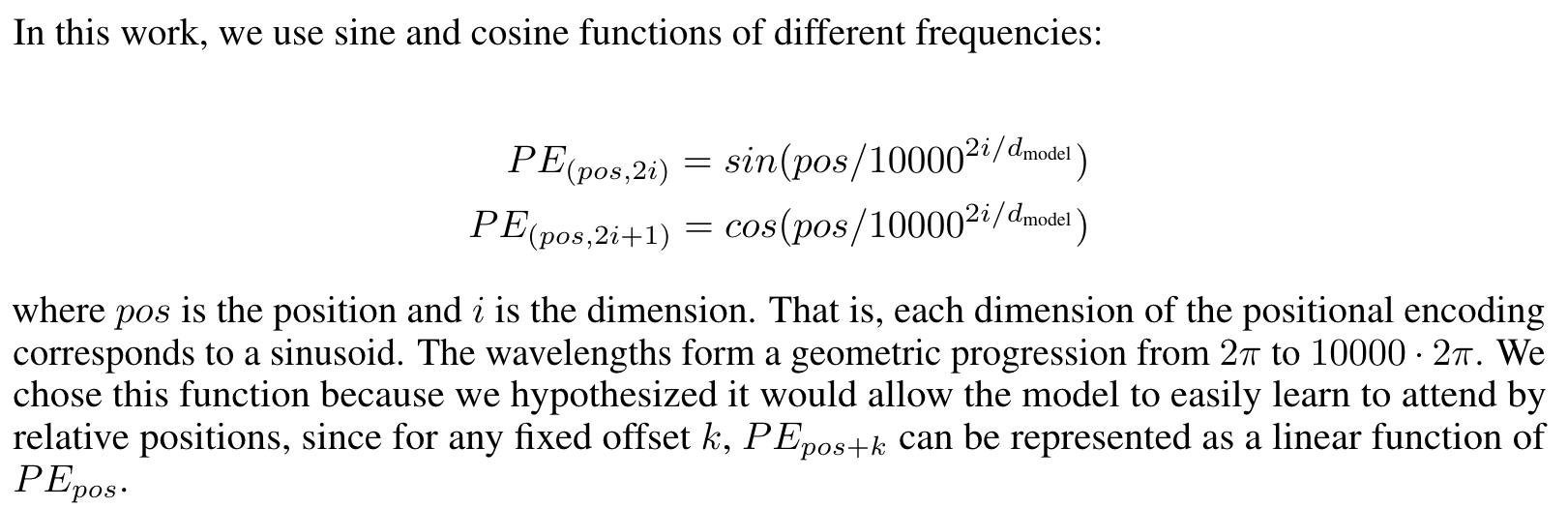
We also experimented with using learned positional embeddings [9] instead, and found that the two versions produced nearly identical results (Page 6)
In terms of computational complexity, self-attention layers are faster than recurrent layers when the sequence length n is smaller than the representation dimensionality d, which is most often the case with sentence representations used by state-of-the-art models in machine translations, such as word-piece [38] and byte-pair [31] representations. (Page 6)
In this work, we presented the Transformer, the first sequence transduction model based entirely on attention, replacing the recurrent layers most commonly used in encoder-decoder architectures with multi-headed self-attention. (Page 10)
一句话总结本文贡献