题目信息
-
Given the heads of two singly linked-lists
headAandheadB, return the node at which the two lists intersect. If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, returnnull.For example, the following two linked lists begin to intersect at node
c1: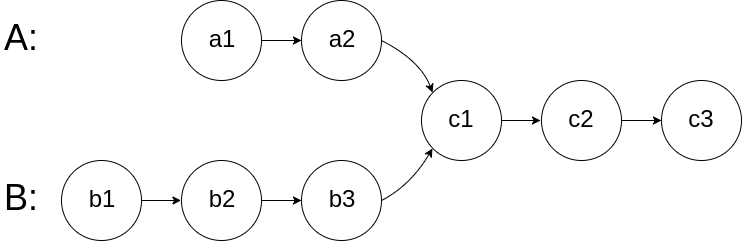
The test cases are generated such that there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
Note that the linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
Custom Judge:
The inputs to the judge are given as follows (your program is not given these inputs):
intersectVal- The value of the node where the intersection occurs. This is0if there is no intersected node.listA- The first linked list.listB- The second linked list.skipA- The number of nodes to skip ahead inlistA(starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.skipB- The number of nodes to skip ahead inlistB(starting from the head) to get to the intersected node.
The judge will then create the linked structure based on these inputs and pass the two heads,
headAandheadBto your program. If you correctly return the intersected node, then your solution will be accepted.Example 1:

Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 Output: Intersected at '8' Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,6,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B. - Note that the intersected node's value is not 1 because the nodes with value 1 in A and B (2nd node in A and 3rd node in B) are different node references. In other words, they point to two different locations in memory, while the nodes with value 8 in A and B (3rd node in A and 4th node in B) point to the same location in memory.Example 2:

Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 Output: Intersected at '2' Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [1,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.Example 3:
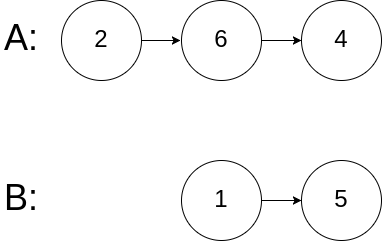
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 Output: No intersection Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values. Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.Constraints:
- The number of nodes of
listAis in them. - The number of nodes of
listBis in then. 1 <= m, n <= 3 * 10<sup>4</sup>1 <= Node.val <= 10<sup>5</sup>0 <= skipA < m0 <= skipB < nintersectValis0iflistAandlistBdo not intersect.intersectVal == listA[skipA] == listB[skipB]iflistAandlistBintersect.
Follow up: Could you write a solution that runs in
O(m + n)time and use onlyO(1)memory? -
描述:
- 给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
解题思路
哈希表
- 将A遍历过的节点放入哈希表中,看B中是否有节点在哈希表中即可
- 需要
的空间复杂度
快慢指针
- 快慢指针空间复杂度可以达到
- 初始状态下,如果两个链表有一个为None,则不会相交
- 使用指针ptA和ptB分别指向A和B,当ptA为None时,移动到headB,当ptB为None时,移动到headA,当ptA和ptB指向同一个节点时,说明找到了重合节点;当ptA和ptB都指向None时,说明不相交
- 注意如果从None移动到另一个链表head,不能继续再移动到next,否则相当于多走了一步
- 设链表A长度为m,链表B长度为n
- 当两个链表不相交时,ptA和ptB都走
个位置同时到达另一方的None - 当两个链表相交,重合部分长度为x,那么当ptA和ptB走到重合起始节点时,ptA走过
,ptB走过 ,刚好同时到达
- 当两个链表不相交时,ptA和ptB都走
代码
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if headA == None or headB == None:
return None
ptA = headA
ptB = headB
while ptA != None or ptB != None:
if ptA == ptB:
return ptA
if ptA == None:
ptA = headB
else:
ptA = ptA.next
if ptB == None:
ptB = headA
else:
ptB = ptB.next
return None
```